The Historical Significance of the Pyramids
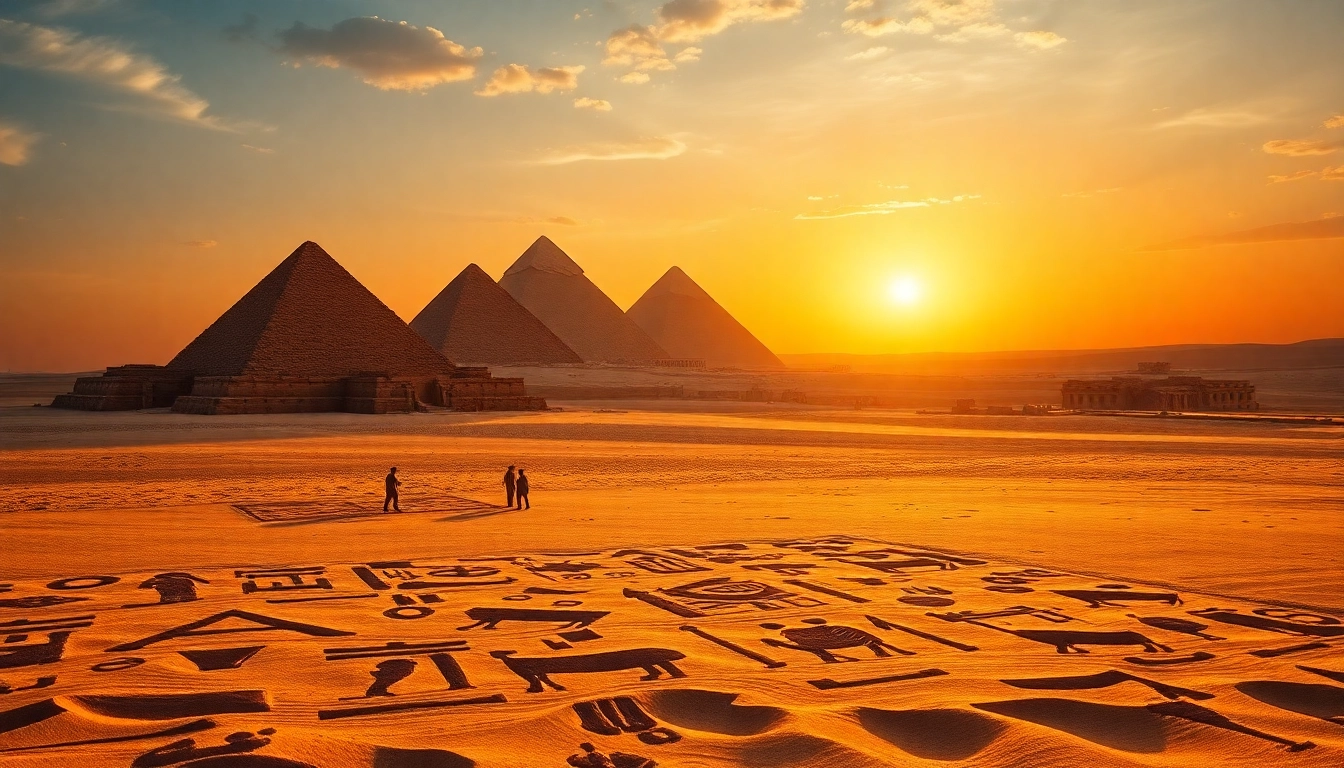
The Egyptian pyramids represent one of the greatest achievements of human civilization and craftsmanship. Towering over the desert plains, these monumental structures have become symbols of ancient engineering prowess and spiritual beliefs. For enthusiasts and scholars alike, the pyramids are more than just relics; they signify the cultural, political, and religious dynamics of ancient Egypt, offering profound insight into a civilization that has captivated people for centuries. According to https://piraminds.com/, this encapsulates the essence of what makes the pyramids indispensable to our understanding of human history.
Overview of Egyptian Civilization
The civilization of ancient Egypt arose around 3100 BCE, and its cultural fabric was woven through a complex interrelation of religion, governance, and societal structure. At the heart of Egyptian civilization were the pharaohs, revered as divine rulers believed to mediate between the gods and humans. Hieroglyphics served as a sophisticated writing system, enabling effective communication and documentation of cultural practices. The Nile River, the lifeblood of Egypt, facilitated agriculture, trade, and transportation, making it a cornerstone of Egyptian prosperity.
Role in Pharaohs’ Afterlife
In ancient Egyptian belief, life did not end with death; rather, it transitioned into a new existence in the afterlife. The pyramids served as monumental tombs designed to protect the deceased pharaohs and their possessions for eternity. Believing that the journey to the afterlife required sustenance and wealth, Egyptians filled their tombs with artifacts, food, and even servants. The intricate architecture of the pyramids not only represented the pharaoh’s power but also their divine status and their continued role in society after death.
Pyramids as Cultural Symbols
The pyramids symbolize much more than mere resting places for pharaohs; they stand as testaments to the engineering capabilities and spiritual beliefs of ancient Egyptians. Over time, various cultures attempted to replicate the pyramid structure, indicating the importance and influence of these monuments across civilizations. The iconic silhouette of pyramids against the Egyptian skyline has become synonymous with ancient Egypt, inspiring countless artists, historians, and tourists who seek to unlock their mysteries.
Construction Techniques: How the Pyramids Were Built
The construction of the pyramids has fascinated historians and archaeologists for centuries. While the exact methods employed remain somewhat shrouded in mystery, newfound discoveries are shedding light on these wonderous feats of engineering.
Materials Used in Pyramid Construction
The primary material used for the pyramids was limestone, with granite utilized for essential structural components and decorative elements. Limestone was often quarried locally and transported to construction sites, while granite was more commonly sourced from Aswan, located hundreds of miles away. The choice of materials allowed the ancient Egyptians to create a durable, magnificent structure that has stood the test of time.
Labor and Workforce Dynamics
Contrary to popular belief, the pyramids were not built by slave labor but rather by a skilled workforce composed of laborers, artisans, and engineers. These workers were often recruited from local communities during the inundation of the Nile, when agricultural activities slowed. Providing fair wages, food, and shelter, the state ensured a steady labor force. Recent archaeological findings suggest that many workers had specialized skills, emphasizing the organized nature of pyramid construction.
Innovative Techniques and Tools
The construction of pyramids involved innovative techniques and precise planning. Large blocks of stone were moved using sledges and lubricated with water to reduce friction. Recent studies indicate that Egyptians devised ramps to transport stones to higher elevations as the pyramid rose. This combination of careful engineering, teamwork, and ingenuity resulted in the iconic structures we see today.
Tourism and Accessibility to the Pyramids
Today, the pyramids attract millions of tourists annually, contributing significantly to Egypt’s economy. However, managing this influx while preserving the integrity of the monuments is an ongoing challenge.
Visitor Experience: What to Expect
Visitors to the Giza Plateau can expect not only to witness the Great Pyramid but also to explore the accompanying structures, including the Sphinx and several smaller pyramids. Guided tours often provide insights into their historical context. Expect to navigate through sensory-rich environments filled with tourists, vendors, and street performances, contributing to a unique cultural experience.
Preservation and Restoration Efforts
Preserving the pyramids is crucial, given their age and vulnerability to environmental factors. Organizations dedicated to conservation use advanced technologies to monitor the structural integrity of the pyramids. Initiatives include restoring eroded areas and ensuring sustainable tourism practices that minimize wear on these ancient structures. Collaborative efforts between local and international experts play a vital role in these initiatives.
Local Economies and Tourism Impact
The economic impact of pyramid tourism extends beyond ticket sales. Local businesses, including hotels, restaurants, and artisanal shops, flourish due to the increased foot traffic. Employment opportunities arise not only in tourism but also in preservation projects, providing a means for local communities to sustain their livelihoods. However, balancing tourism with preservation remains an ongoing debate within the affected communities.
Modern Discoveries and Their Implications
Recent archaeological advancements and technologies have transformed our understanding of the pyramids. New findings continue to yield surprising insights into ancient Egyptian life and construction methods.
Recent Archaeological Findings
Excavations and explorations of the pyramid complex have unearthed significant finds, such as ancient tools and historical artifacts. In recent years, non-invasive techniques, including muon tomography, have revealed hidden voids and chambers within the pyramids. These discoveries not only provide insights into construction methods but also aid in understanding the rituals associated with burial practices.
Theories About Hidden Chambers
Many researchers speculate about the potential existence of undiscovered chambers within the pyramids, which could contain important artifacts. While some theories suggest these spaces may have been left intentionally or were never completed, continuous exploration could rally new evidence that reshapes our understanding of these monumental tombs.
Technological Advances in Research
Technological progress has drastically altered archaeological practices. Tools like 3D scanning, drones, and geophysical surveys have provided researchers with a clearer picture of the pyramids’ structure without excavation. These advances make it easier to document changes over time and predict how environmental factors affect the pyramids, aiding conservation efforts.
FAQs: Understanding Common Queries
What are the Great Pyramids?
The Great Pyramids are monumental tombs built in ancient Egypt, specifically the Pyramids of Giza, constructed around 2580 to 2560 BCE. They served as burial sites for pharaohs, reflecting their status and beliefs about the afterlife.
How did they get built?
Constructed using locally sourced limestone and granite, the pyramids were built by skilled laborers who used ramps and sledges to transport massive stone blocks. Recent discoveries reveal sophisticated engineering techniques were involved.
Are the pyramids aligned with stars?
Yes, many pyramids, including those at Giza, exhibit precise alignment with celestial bodies. For example, their layout corresponds to the orientations of significant stars, highlighting the Egyptians’ advanced understanding of astronomy.
Can you enter the pyramids?
Yes, some pyramids allow visitors to enter, including the Great Pyramid. However, access may vary due to preservation efforts, and you should always check ahead for current visitor policies.
What is the best time to visit?
The best time to visit the pyramids is from October to April when the weather is cooler. Visiting early in the morning or late in the afternoon can also help avoid crowds and heat.